Soil testing and formula fertilization technical specification (Trial) National Agricultural Technology Extension Service Center May 25 1 Scope This specification specifies the field experiment of fertilizer effect, the collection and preparation of soil samples, the investigation of basic conditions in the field, soil and plant testing, fertilizer formulation design, reasonable use of formula fertilizer, effect feedback and evaluation, data summary and report writing Content and operating procedures. This specification applies to soil testing and formulated fertilization techniques in different regions, different soils, and different crops. 2 Reference standards This specification refers to the following countries or industry standards. GB 15063 compound fertilizer (compound fertilizer) GB 18877 organic-inorganic compound fertilizer GB/T 6274 Fertilizer and Soil Conditioner Terminology NY/T 496 Fertilizer Fair Use Guidelines NY/T 497 Fertilizer Effect Identification Field Test Technical Regulations NY/T 85 Soil organic matter determination potassium dichromate titration NY/T 53 soil total nitrogen determination 3 Terms and Definitions The following terms and definitions apply to this technical specification. 3.1 Soil testing and formulated fertilization Testing soil for formulated fertilization Soil testing and fertilization are based on soil testing and fertilizer field trials. Based on the laws of crop manure requirements, soil nutrient properties and fertilizer effects, based on the rational application of organic fertilizers, nitrogen is proposed. The application amount of fertilizers such as phosphorus, potassium, and medium and trace elements, fertilizer application period, and application methods. 3.2 Fertilizer fertilizer to provide plant nutrients into its main efficacy materials (2.1.2 of GB/T 6274-1997). 3.3 Organic fertilizers Organic fertilizers are mainly derived from plants and (or) animals and are applied to the soil to provide carbonaceous materials with plant nutrition as its main function (2.1.4 of GB/T 6274-1997). 3.4 Inorganic [mineral] fertilizer Inorganic [mineral] fertilizer is a nutrient in the form of inorganic salts, extracted by physical, and/or chemical methods. It is customarily called inorganic fertilizer (2.1.3 of GB/T 6274-1997). 3.5 Single fertilizer straight fertilizer Nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium three nutrients, only a nutrient marked amount of nitrogen fertilizer, phosphate fertilizer and potash fertilizer generic term. (2.1.16 of GB/T 6274-1997). 3.6 a large number of elements macro-element The general term for nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium. 3.7 The element of secondary element The general term for calcium, magnesium, and sulphur elements. 3.8 Trace element, micronutriment The micronutriment is a necessary but relatively small element for plant growth, such as boron, manganese, iron, zinc, copper, molybdenum, etc. (GB/T 6274-1997, 2.1.25.3). 3.9 Nitrogenous fertilizer/ nitrogen fertilizer With nitrogen (N) in the amount indicated to provide plant nitrogen nutrients into its single function of a single fertilizer. 3.10 Phosphate phosphate fertilizer/phosphatic fertilizer With the indicated amount of phosphorus (P2O5) to provide a single fertilizer with plant phosphorus as its main function. 3.11 Potash fertilizer has the indicated amount of potassium (K2O) to provide a single fertilizer for plant potassium nutrients. 3.12 compound fertilizer N, P, K three kinds of nutrients, at least two kinds of nutrient content of the chemical method and (or) blended method of fertilizer (GB/T 6274-1997 2.1. 17). 3.13 complex fertilizer N, P, K three kinds of nutrients, at least two kinds of nutrient content of the chemical fertilizer only made of fertilizer (GB/T 6274-1997 2.1.18). 3.14 blended fertilizer Among the three nutrients of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium, there are at least two kinds of nutrient-labeled fertilizers made by the dry-blending method, which is a kind of compound fertilizer (3.3 in GB 15063-2001). . 3.15 plant nutrient plant nutrient The chemical elements necessary for plant growth (GB/T 6274-1997 2.1.24). 3.16 Fertilizer Nutrients fertilizer nutrient Fertilizers are provided in the plant nutrient (2.1.25 in GB/T 6274-1997). 3.17 Fertilizer effect Fertilizer effect is the effect of fertilizer on crop yield. It is usually expressed in terms of the increase in crop yield and the benefits that can be obtained by the application amount of nutrients per unit of fertilizer. (3.23 in NY/T 496-2002) 3.18 dosing rate; dose: The mass or volume of fertilizer or soil conditioner or nutrient applied to cultivated land or per unit mass of growth medium per unit area (2.1.23 of GB/T 6274-1997). 3.19 Conventional fertilization It is also known as custom fertilization, which refers to the average amount of fertilization in the previous three years (mainly nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium fertilizers), fertilization varieties, and fertilization methods (3.5 in NY/T 497-2002). 3.20 Check control (control) refers to no fertilizer treatment, which is used to determine the absolute value of the fertilizer effect, to evaluate the natural soil productivity and to calculate the fertilizer utilization rate. 3.21 Formulated fertilizer Formulated fertilizer is based on soil testing and fertilizer field trials. It is formulated with various simple fertilizers and/or compound fertilizers as raw materials according to the laws of crop manure requirements, soil fertility and fertilizer effects. Regional, specific crop fertilizers.
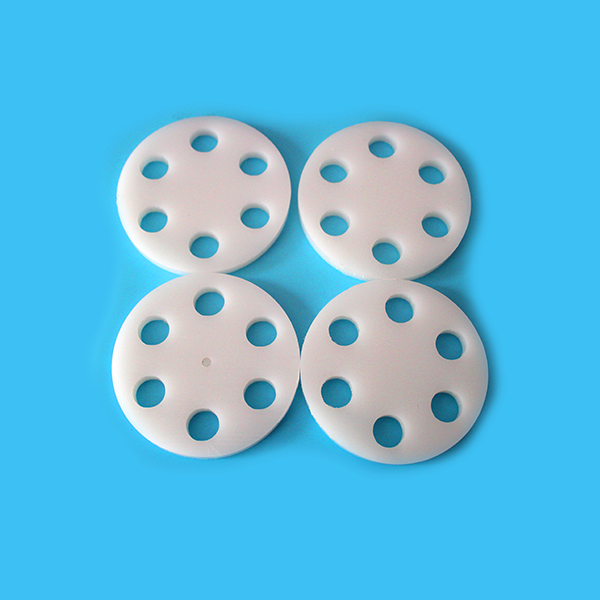
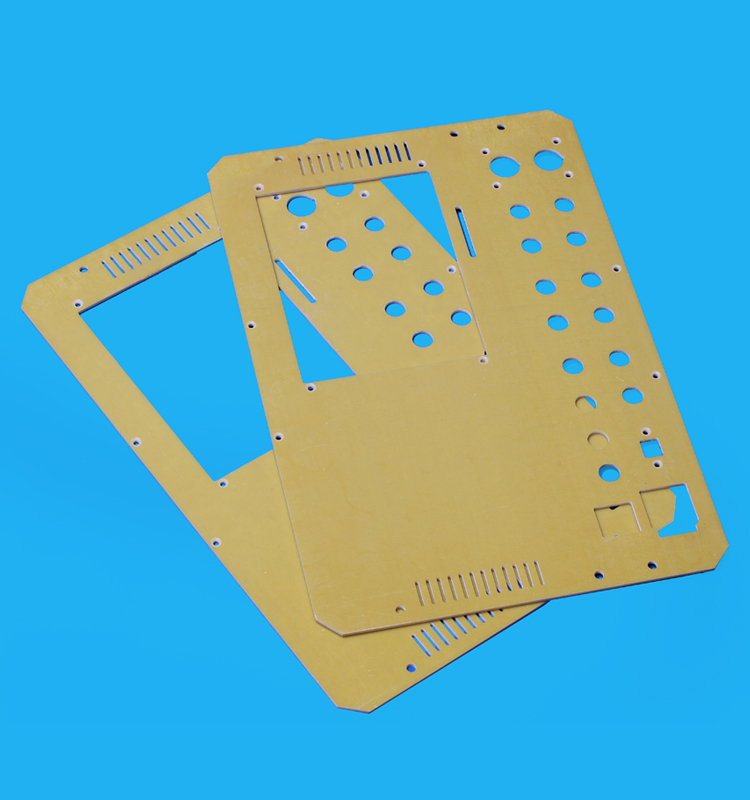
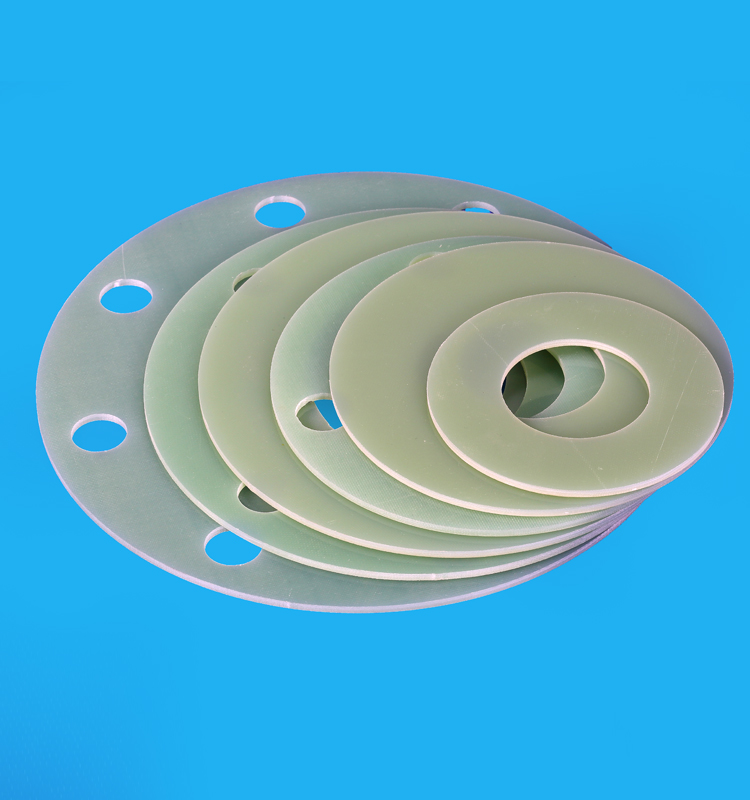
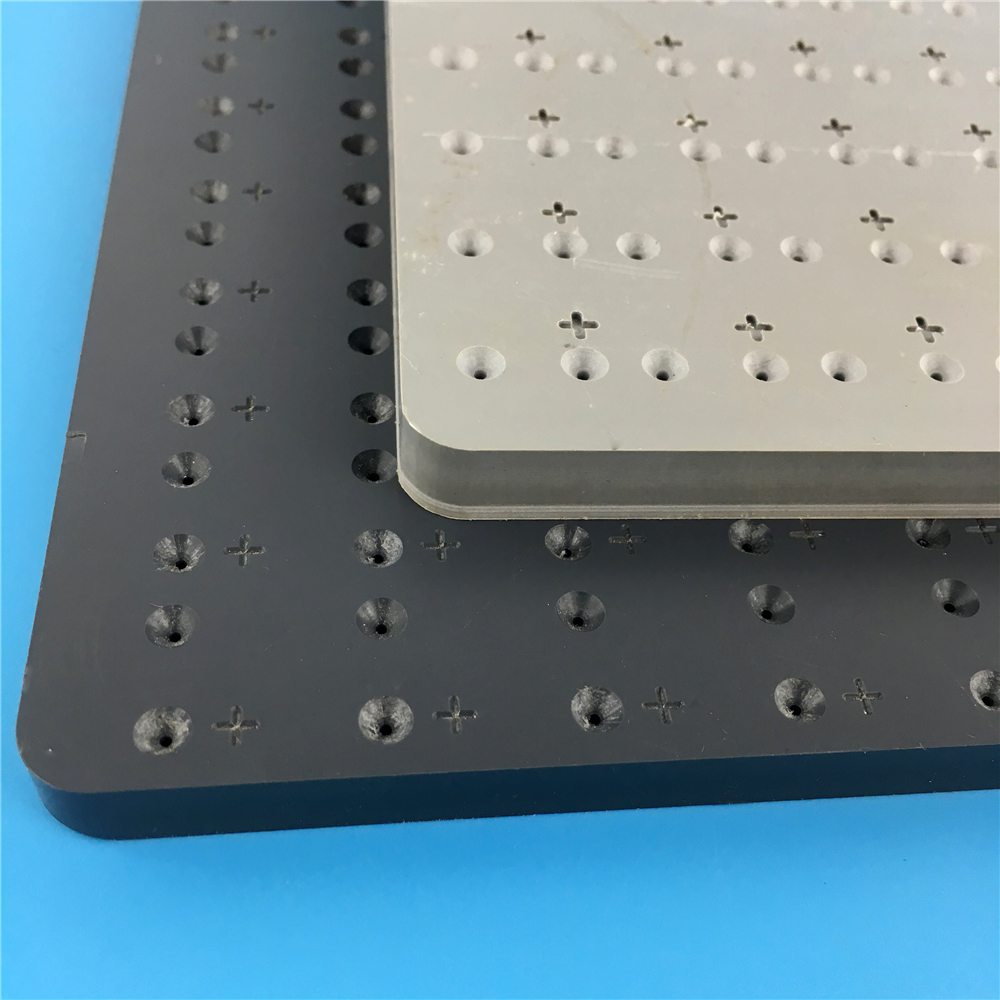
Based on most advanced machining technology and manufacture equipment, we are offering post machining of plastics service in tune with highest standards. We understand engineering plastics, and we are highly renowned for rich industrial experience. Therefore, we are able to cater to your discerning machining needs in either trial orders or mass production.
Additionally, we are equipped with various machines such as 7 CNC machining centers, 4 CNC lathes, 1 manually controlled lathes, 2 drilling machines, 3 grinding machines, 3 cutting machines and 2 carving machine.
Machinery Equipments:
* CNC engraving machine, for cutting,carving a variety of insulation materials.
* Laser cutting machine, for acrylics mostly .
* Sawing machine, for cutting all kinds of plastic and insulation products..
Processing Crafts:
1.Bending & Gluing
2.CNC Routing & Machining
3.CNC Saw Cutting
4.Drilling and Tapping
5.Plastic Welding
Available Processing Materials:
FR4/3240 Epoxy sheet, phenolic cotton/paper sheet, Bakelite Sheet, NYLON, POM, PP, PVC , ABS , PTFE, PE etc.
Bakelite Products Processing, Plastic Products Processing, Processing Product, Laminates Processing Product SHENZHEN XIONGYIHUA PLASTIC INSULATION LTD , https://www.xyhplastic.com